Physics: Waves - Topic Review
Table of Contents
Definitions
- Medium: the material through which a wave travels
Wave Properties
- Vibrating objects transfer energy through waves
- Waves are classified by what they move through
- There are two types: mechanical and electromagnetic
Mechanical Waves
- Mechanical waves transfer energy through vibrations in a medium
- Examples include water, sound and wind
- A wave can be a single pulse, or continuous
Waves only transfer energy from one point to another. THEY DO NOT TRANSFER MATTER! However, matter may move as the wave passes through it.
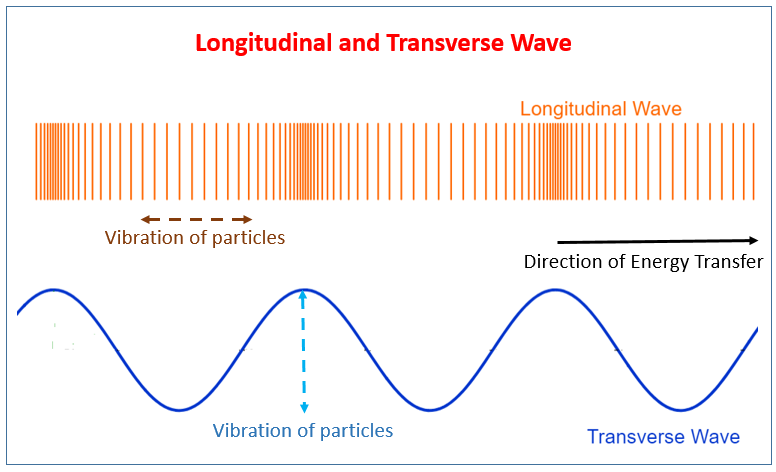
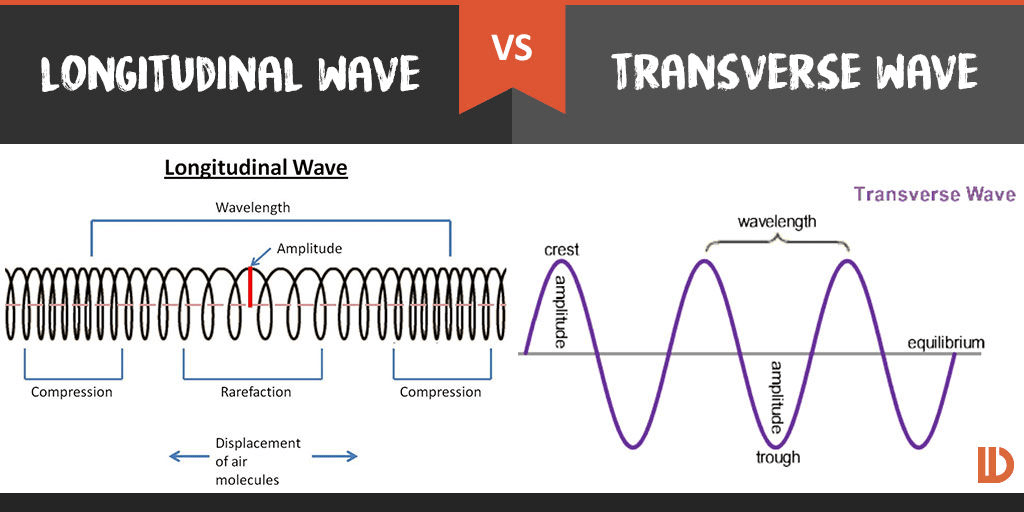
- Mechanical waves can be either transverse or longitudinal.
- In a transverse wave, particles oscillate (move back and forth) perpendicular (at 90°) to the direction of energy transfer.
- In a longitudinal wave, particles move parallel to the direction of energy transfer.
- This simulation demonstrates a wave - PHET COLORADO
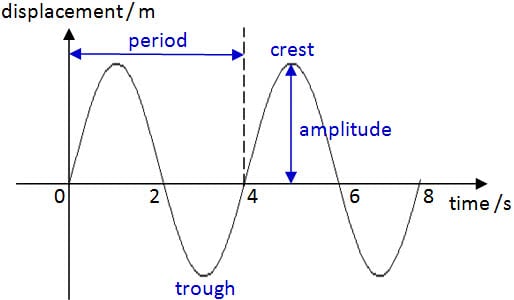
Measuring Mechanical Waves
- Waves can be represented by displacement-distance graphs and displacement-time graphs.
- The graph takes a sinusoidal shape (like a sine wave)