title: Science - Space Year 10 layout: draft categories:
- Year 10
- Science tags:
- Year 10
- Science
- Space
- Review date: 2019-10-25 12:26:00 math: true
Definitions
- Absolute magnitude: the brightness of an object when viewed from a fixed distance
- Used to eliminate the brightness differences caused by distance
- Relative brightness: brightness when viewed from earth
- Star: A ball of gas held together by gravity
- Nebula: An interstellar cloud of dust, hydrogen, helium and other ionized gases
- Solar System: a central sun with its associated planets, asteroids, meteors, satellites (i.e. ,moons), and comets that are “captured” in its orbit.
- Galaxy: A huge collection of gas, dust, and billions of stars and their solar systems, held together by gravity
Life cycle of a star
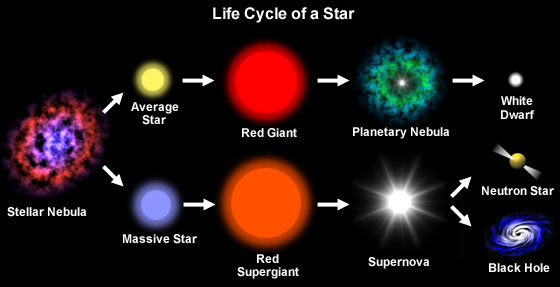
- Most stars occur in the MAIN SEQUENCE
- After they run out of Hydrogen to fuse, main sequence stars will expand, turning into a RED GIANT, and will start to fuse Helium
- Once their Helium supply runs out, the star will expel its outer layers in a PLANETARY NEBULA. At the core of this nebula is the remains of the star: a WHITE DWARF
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagrams

- Shows the color vs temperature vs lifespan vs absolute magnitude
Scale of the Universe
- Interstellar distances are measured in LIGHT YEARS
- 1 Light Year = about 9.5 trillion km
- Further distances can also be measured in PARSECS
- 1 parsec = 3.26 Light Years = 31 trillion km